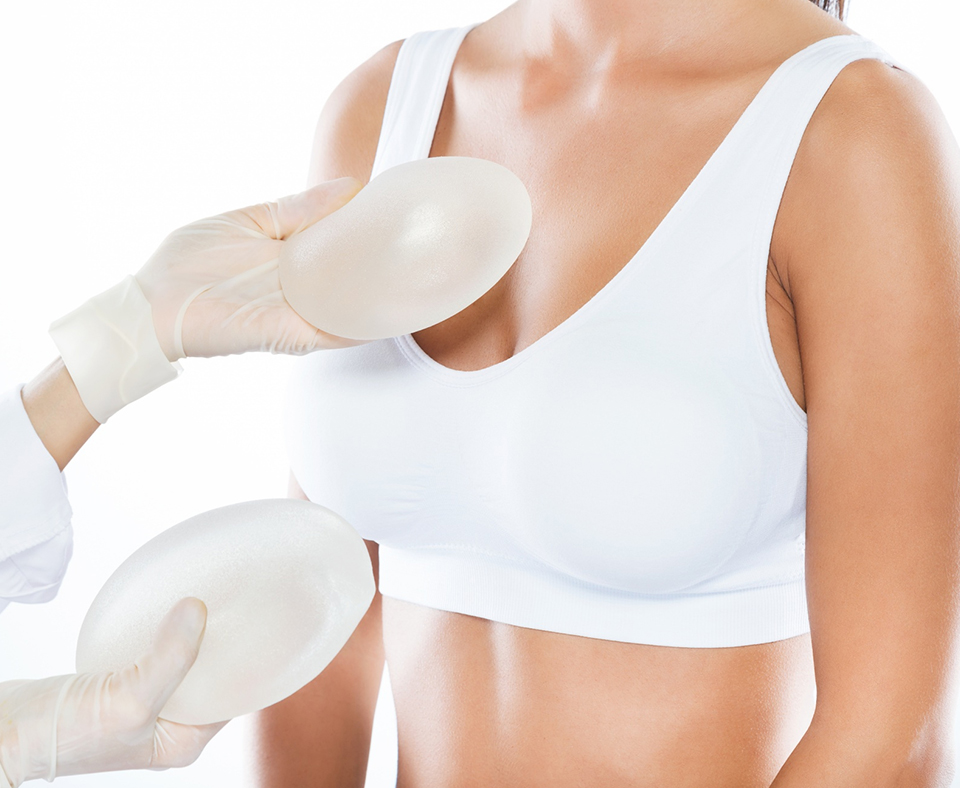
Breast augmentation, also known as augmentation mammoplasty, is a surgical procedure that aims to increase the size and enhance the shape of the breasts. This is achieved through the placement of breast implants, which are typically made of silicone or saline.
Breast augmentation can be performed for a variety of reasons, including to enhance breast size and shape, correct breast asymmetry, or restore breast volume lost due to weight loss, pregnancy, or aging.
The procedure involves making an incision, usually in the crease under the breast or around the areola, and inserting the breast implant either under the breast tissue or under the chest muscle. The incision is then closed with sutures.
A good candidate for breast augmentation is someone who is in good overall health, has realistic expectations about the outcome of the surgery, and is seeking to enhance the size and shape of their breasts. It is important that the candidate has fully developed breasts, is not currently pregnant or breastfeeding, and has a stable body weight. Candidates should also be aware that breast augmentation may require additional surgeries in the future to replace or remove the implants.


